Explore web search results related to this domain and discover relevant information.

But the launch of SpaceX’s 10th test flight was scrapped after there was an issue with the ground systems. "Standing down from today's tenth flight of Starship to allow time to troubleshoot an issue with ground systems," the company said on X, offering no other information. This came after multiple failures ...
But the launch of SpaceX’s 10th test flight was scrapped after there was an issue with the ground systems. "Standing down from today's tenth flight of Starship to allow time to troubleshoot an issue with ground systems," the company said on X, offering no other information. This came after multiple failures in recent years — including three disastrous explosions in 2025 alone.Between January and June, SpaceX suffered four Starship setbacks — a dramatic explosion in its first test flight, a midair blast in the second, a fiery destruction in the third and finally a ground-test explosion following those in-flight failures.In the past, Musk has admitted that repeated setbacks are part of SpaceX’s rapid test-and-fail approach.SPACEX'S STARSHIP FLIGHT 9 ENDS IN FAILURE AFTER BOOSTER LOSS: 'SUCCESS COMES FROM WHAT WE LEARN

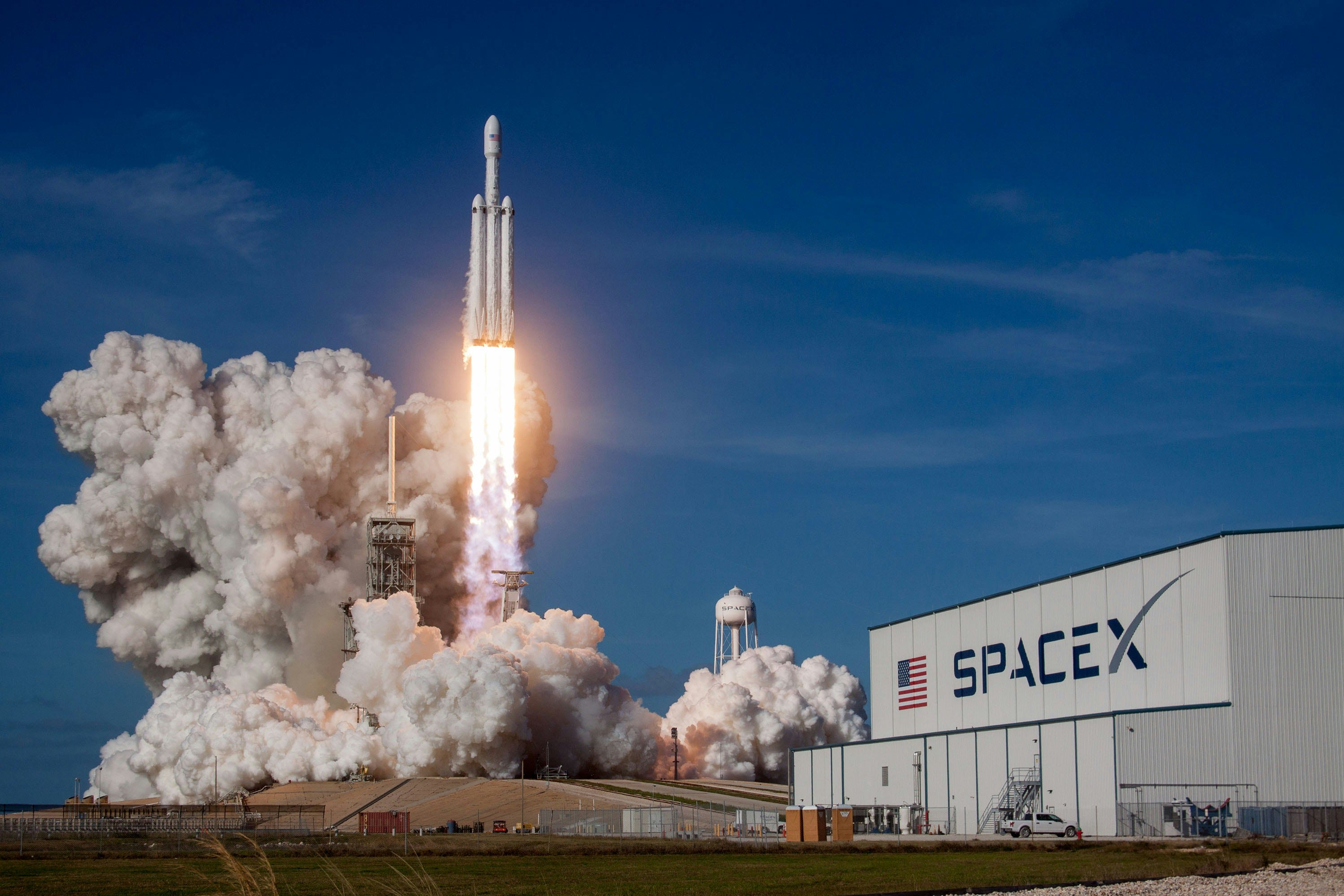
Elon Musk, SpaceX's founder and CEO, presented an update on Starship to company employees in May. This chart shows the planned evolution from Starship Version 2 (left) to Version 3 (middle), and an even larger rocket (right) in the more distant future. The FAA said Friday it formally closed the investigation into Starship's most recent in-flight failure ...
Elon Musk, SpaceX's founder and CEO, presented an update on Starship to company employees in May. This chart shows the planned evolution from Starship Version 2 (left) to Version 3 (middle), and an even larger rocket (right) in the more distant future. The FAA said Friday it formally closed the investigation into Starship's most recent in-flight failure in May, when the rocket started leaking propellant after reaching space, rendering it unable to complete the test flight.Finally, detecting a major problem, Starship triggered automatic onboard commands to vent all remaining propellant into space and "passivate" itself before an unguided reentry over the Indian Ocean, prematurely ending the test flight. Engineers recreated the diffuser failure on the ground during the investigation and then redesigned the part to better direct pressurized gas into the main fuel tank.SpaceX said COPVs on upcoming flights will operate at lower pressures, and managers ordered additional inspections on COPVs to look for damage, more proof testing, more stringent acceptance criteria, and a hardware change to address the problem. This year began with the first launch of an upgraded version of Starship, known as Version 2 or Block 2, in January. But the vehicle suffered propulsion failures and lost control before the upper stage completed its engine burn to propel the rocket on a trajectory carrying it halfway around the world to splash down in the Indian Ocean.SpaceX tried to experiment with new ways of landing the Super Heavy booster on the last test flight, too. The Super Heavy exploded before reaching the ocean, likely due to a structural failure of the rocket's fuel transfer tube, an internal pipe where methane flows from the fuel tank at the top of the rocket to the engines at the bottom of the booster.
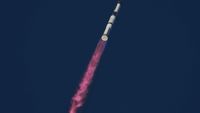
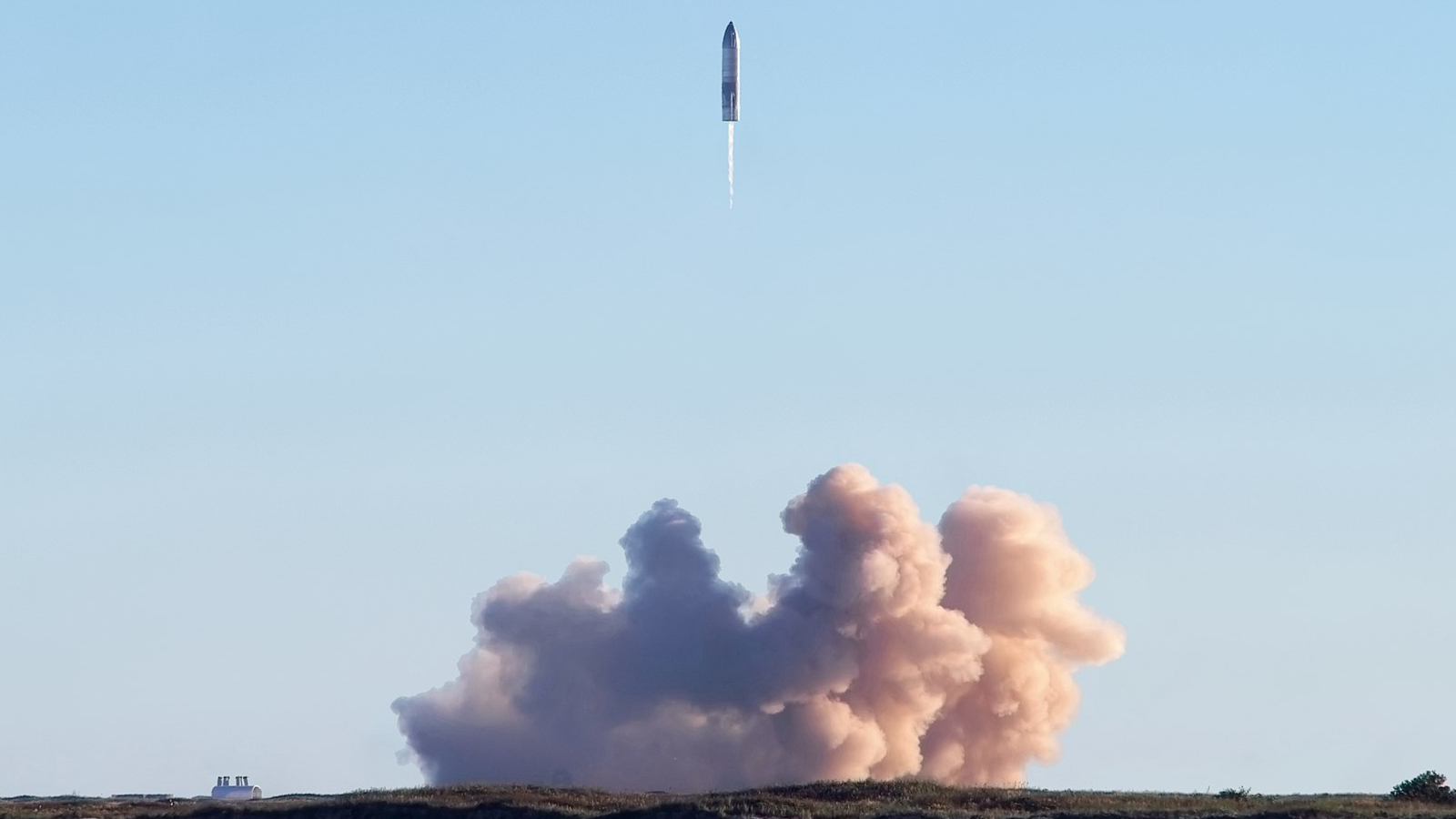
SpaceX’s Starship has successful 10th flight test After a series of failures during recent test flights, SpaceX's massive Starship had a smooth ride for Tuesday's blastoff and successfully deployed some fake satellites.
SpaceX's massive Starship rocket racked up some much-needed successes on its 10th test flight, hitting key test objectives and breaking a streak of failures that bedeviled the spaceship this year.SpaceX also wants to use Starship to deploy a huge number of its Starlink satellites. But on the last test flight the ship's payload bay door failed to open.As planned, the rocket's lower stage returned to Earth and briefly hovered over the waters of the Gulf before splashing down. After deploying the satellite simulators, the upper stage reentered the Earth's atmosphere, allowing SpaceX to study the performance of its heat shield and flaps, which Huot noted looked a little "toasty."This smooth flight was very different from three tests earlier this year, which saw the upper stage of the rocket explode or disintegrate for various reasons, much to the dismay of many in the space community.
Test flight comes after explosive failures raised doubts over founder Elon Musk’s goals to reach Mars and moon ... Third time was the charm on Tuesday for the launch of SpaceX’s Starship megarocket after the launch had been scrubbed two times in as many days.
Shortly after reaching space, Starship’s “Pez”-like satellite deployment system dispensed mock Starlink satellites for the first time, a milestone SpaceX either cancelled or failed to reach during past tests.The 10th test flight comes after a string of explosive failures that raised doubts about whether the world’s most powerful launch vehicle can fulfill founder Elon Musk’s vision of colonizing Mars or helping Nasa return astronauts to the moon. SpaceX will not attempt to catch the booster from Tuesday’s flight because the component would instead be used for in-flight experiments “to gather real-world performance data on future flight profiles and off-nominal scenarios”.This year, two Starship tests have failed early in flight, with another failure in space on its ninth flight, and a “catastrophic explosion” of test stand in June that destroyed a Starship and sent debris flying into nearby Mexican territory have tested SpaceX’s capital-intensive test-to-failure development approach, in which new iterations of rocket prototypes are flown to their technical limits.Despite recent setbacks, Starship is not seen as being at a crisis point. SpaceX’s “fail fast, learn fast” philosophy has already given it a commanding lead in launches with its Falcon rockets, while Dragon capsules ferry astronauts to the International Space Station and Starlink has become a geopolitical asset.

They are trying to push the vehicle ... things fail. Similar testing is done with aircraft, they test shutting down engines mid flight, test disabling some of the breaks/thrust reversers on landing, even test evacuating a full flight with half of the exits blocked. One of the things SpaceX needs ...
They are trying to push the vehicle to its limits and if they want the vehicle to carry humans, they not only need to demonstrate that Starship is inherently reliable, but that it can also still accomplish its mission / carry things safely even when things fail. Similar testing is done with aircraft, they test shutting down engines mid flight, test disabling some of the breaks/thrust reversers on landing, even test evacuating a full flight with half of the exits blocked. One of the things SpaceX needs to do to get high numbers of people to trust Starship as a means of transportation is to demonstrate that it is extremely safe, not just in nominal operations but in off-nominal operations.Everything else is just noise, from SpaceX's perspective. ... I guess, with so much public attention and I'd like to think a broad desire for success of the project, I would want to set expectations and meet or exceed them - and thus generate further enthusiasm for the project. I know, it is probably a bit entitled for me to be sitting here in my lounge chair and expect to get the details of what is success or failure in this program.If they set some arbitrary limit, there will be pressure to stop testing after that number even if they haven't learned everything they need to learn to make the vehicle as safe and as capable as possible. Or they will conduct the additional tests they need and they get bad press for failing to have an operational vehicle within the promised number of tests. SpaceX is remarkable open for a private company about what they are doing and how they are doing it.That makes a little more sense. There’s a lot of logic in expected failure when you’re using old stock and testing limits. Now I’m curious when they will be testing gen 3 More replies ... SpaceX ist accountable to its investors only.

This chart shows the planned evolution ... into Starship's most recent in-flight failure in May, when the rocket started leaking propellant after reaching space, rendering it unable to complete the test flight....
Elon Musk, SpaceX's founder and CEO, presented an update on Starship to company employees in May. This chart shows the planned evolution from Starship Version 2 (left) to Version 3 (middle), and an even larger rocket (right) in the more distant future. The FAA said Friday it formally closed the investigation into Starship's most recent in-flight failure in May, when the rocket started leaking propellant after reaching space, rendering it unable to complete the test flight.Engineers recreated the diffuser failure on the ground during the investigation and then redesigned the part to better direct pressurized gas into the main fuel tank. This will also "substantially decrease" strain on the diffuser structure, SpaceX said.SpaceX said COPVs on upcoming flights will operate at lower pressures, and managers ordered additional inspections on COPVs to look for damage, more proof testing, more stringent acceptance criteria, and a hardware change to address the problem. This year began with the first launch of an upgraded version of Starship, known as Version 2 or Block 2, in January. But the vehicle suffered propulsion failures and lost control before the upper stage completed its engine burn to propel the rocket on a trajectory carrying it halfway around the world to splash down in the Indian Ocean.SpaceX tried to experiment with new ways of landing the Super Heavy booster on the last test flight, too. The Super Heavy exploded before reaching the ocean, likely due to a structural failure of the rocket's fuel transfer tube, an internal pipe where methane flows from the fuel tank at the top of the rocket to the engines at the bottom of the booster.
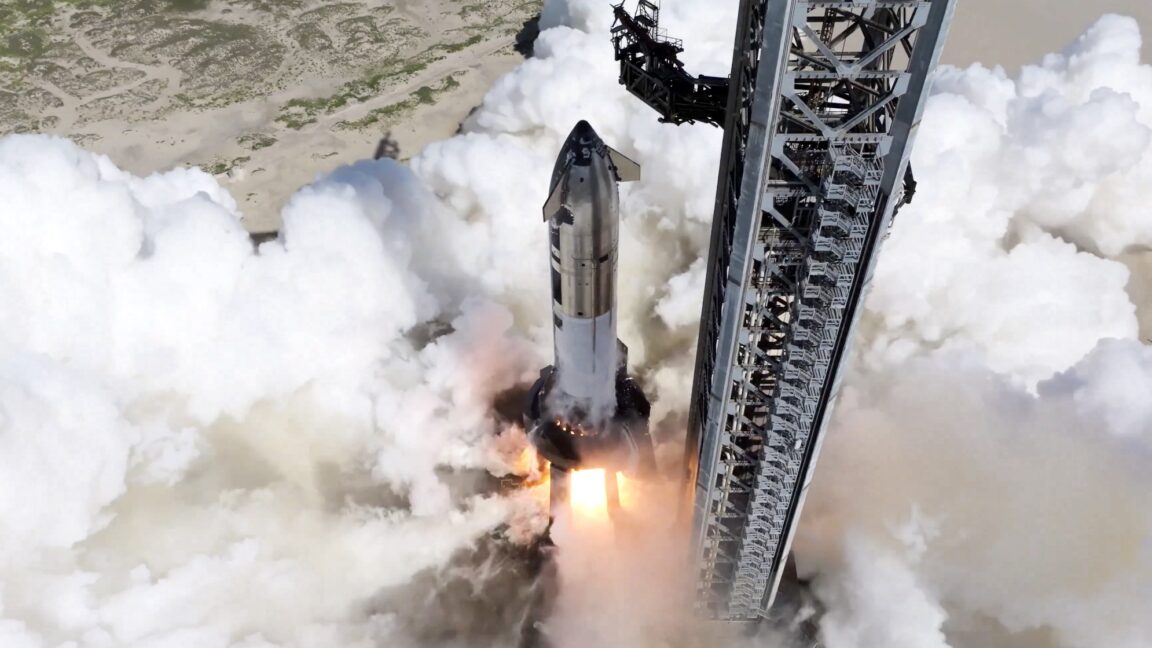


SpaceX has had a long journey through 10 flight tests of Starship. Teams have endured explosions and failures, but also achieved triumphs through amazing reentries, catches of Boosters, and even the reuse of a Booster.
Booster 14-2 completed almost all of its objectives, but it was lost during the landing burn startup because SpaceX was trying to push the limits of the Booster, and it did not survive. Ship 35 passed SECO but lost control during the coast phase due to a methane gas leak into the payload bay, resulting in loss during an uncontrolled reentry. This gas leak was due to a failure of the diffuser and canister assembly at the top of the forward dome.The second was an in-space burn of a Raptor engine for Block 2. Despite damage to the aft section and aft flaps due to possible issues with the engine chill lines, Ship 37 survived reentry and landed within three meters of the target zone. After the three straight failures to start 2025, this flight was a massive success and a morale boost to SpaceX.SpaceX has had a long journey through 10 flight tests of Starship. Teams have endured…During the launch, a hole under the launch mount occurred because the water deluge system had not been installed yet. SpaceX took a gamble to fly Flight 1 before the installation of this system, hoping the fondag concrete would hold for a single flight; it did not, however.
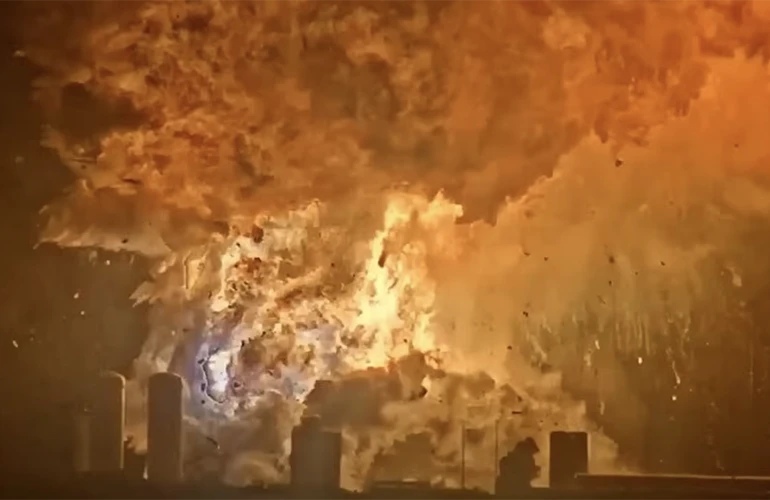
At 11 p.m. on June 18, 2025, SpaceX engineers initiated what should have been a routine six-engine static fire test — a ground test for an upcoming launch — at Starbase’s Massey test site. Instead, Ship 36 experienced a catastrophic failure during propellant loading, which Elon…
At 11 p.m. on June 18, 2025, SpaceX engineers initiated what should have been a routine six-engine static fire test — a ground test for an upcoming launch — at Starbase’s Massey test site. Instead, Ship 36 experienced a catastrophic failure during propellant loading, which Elon Musk attributed to a nitrogen COPV failure “below its proof pressure.”While SpaceX emphasized that “there are no reported injuries, and all personnel are safe,” the explosion is part of a pattern visible in their own mission updates: Flight 7 in January (which SpaceX attributed to “harmonic response” causing propellant leaks), Flight 8 in March (where the company noted “inadvertent propellant mixing and ignition”) and Flight 9 in May (resulting in what SpaceX called “loss of attitude control” from propellant leaks). Each failure is different, each documented in carefully minimized language, each adding to a pattern that R&D professionals recognize as something more significant than isolated “anomalies.”The financial costs of the failures, writ large, are significant. At $90-100 million per vehicle, SpaceX has destroyed over half a billion dollars in Starship hardware since 2023 alone. Yet the true program cost is far higher: Musk stated SpaceX would spend $2 billion on Starship in 2023 alone, with total program investment exceeding $5-6 billion since development began.The pattern of Starship failures underscores a key point: When iteration cycles don’t build on each other, the results aren’t pretty. Each of the four recent failures stemmed from a different root cause, suggesting that SpaceX’s rapid testing cadence may be outpacing its ability to fully understand and address systemic issues.

The added muscle for Starship is ... can produce more of the rockets, one of the people said. SpaceX revealed in August that a pressurized bottle holding gaseous nitrogen had been damaged, causing it to fail and lead to an explosion during fueling....
The added muscle for Starship is intended to help improve the craft’s reliability and individual component testing, as well as the rate at which the company can produce more of the rockets, one of the people said. SpaceX revealed in August that a pressurized bottle holding gaseous nitrogen had been damaged, causing it to fail and lead to an explosion during fueling.Those failures have led to increasing questions about whether Starship will be able to fulfill Musk’s aims. A New York Magazine story asked: “Is Elon Musk’s Starship Doomed?” · SpaceX’s impressive track record, including the construction of the Starlink satellite-internet network and its innovation on reusable rocket technology, has had a deep impact on the space industry and US space policy.Its process is designed to learn from failures fast. Yet Starship’s recent struggles are revealing how rapidly updating rockets that cost hundreds of millions to make can lead to a cascade of expensive issues. “When you’re changing lots of things in the design at once, all of those ripple effects start adding up,” said Todd Harrison, a senior fellow at the American Enterprise Institute who focuses on space policy.It's possible that SpaceX will be able to continue to absorb more testing failures, but the perception that the company is moving forward in Starship development will be key to their long-term investment success and fulfilling contractual agreements with NASA.
SpaceX Will Fail The company is overstretched and poorly managed. Icarus may have had wax wings, but imagine if he was also a racist neo-Nazi with more money than God. Well, that is precisely what is …
You see, rather than flying too close to the sun, Musk has claimed that it’s a shiny pot of gold and flown directly towards its orbit, failing to notice that his wings may have already melted away. SpaceX is set to fail; the question isn’t “if” but “when.” Let me explain.It didn’t have to be this way, but Musk has chosen to bet the entire company’s future on the project. Why? Well, Starship is SpaceX’s only viable route to increasing profits, and SpaceX needs these massive profits to repay the huge amount of investment dumped into Starship.


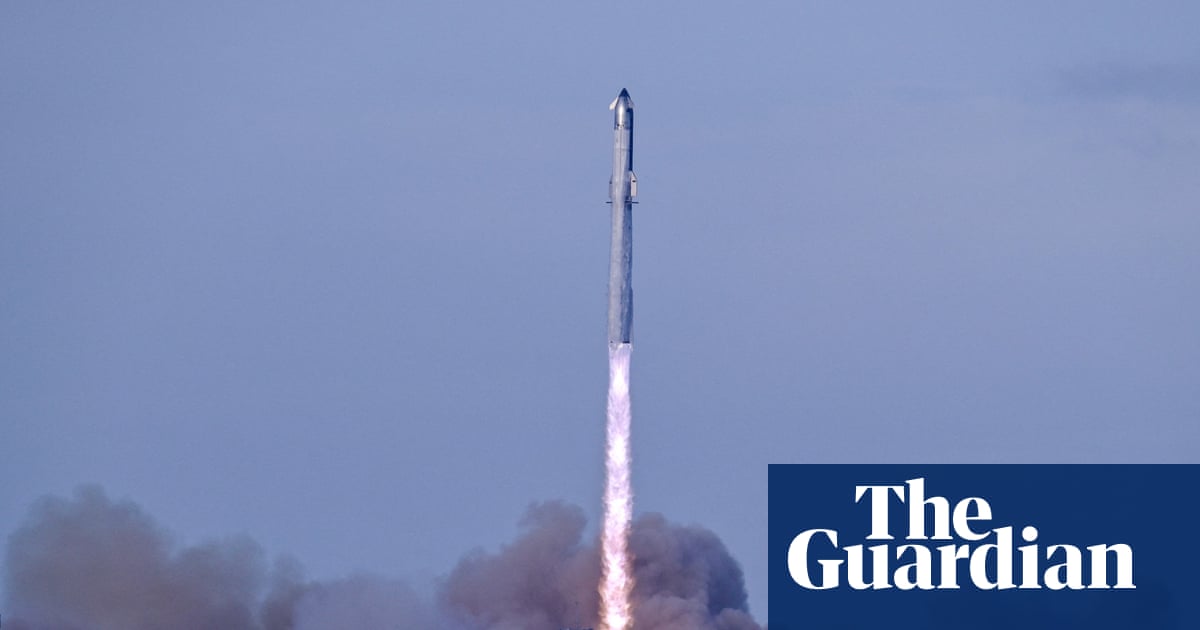
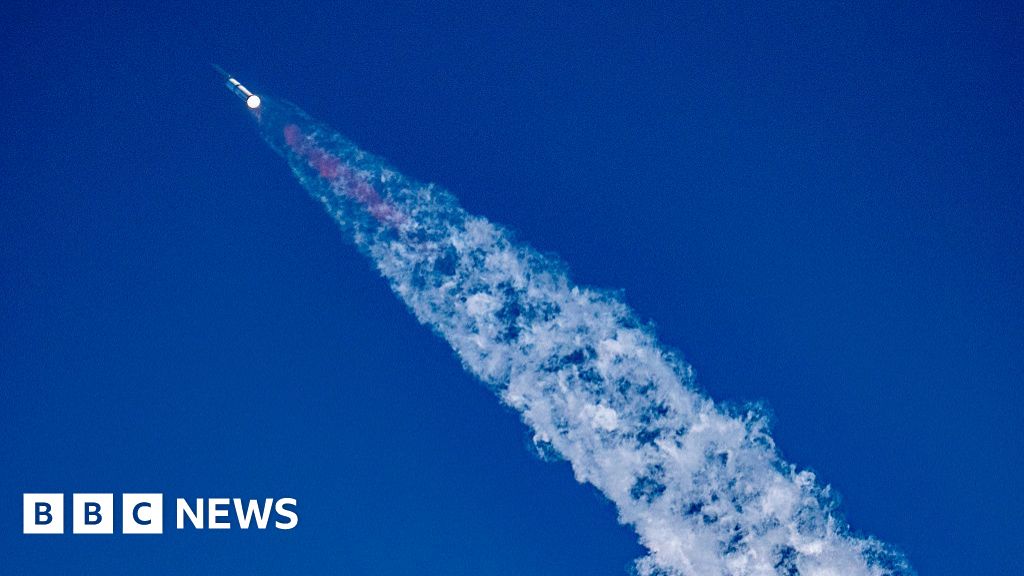
The test aims to show that the mammoth rocket is capable of achieving key flight goals.CreditCredit...SpaceX, via Associated Press ... Aug. 26, 2025 · After several disappointing failures, SpaceX’s Starship — the mammoth rocket that Elon Musk hopes to use to take people to Mars — made ...
The test aims to show that the mammoth rocket is capable of achieving key flight goals.CreditCredit...SpaceX, via Associated Press ... Aug. 26, 2025 · After several disappointing failures, SpaceX’s Starship — the mammoth rocket that Elon Musk hopes to use to take people to Mars — made it all the way up to space and all the way back down to Earth during a 10th test flight on Tuesday night.SpaceX has a “break it and fix it” philosophy of development, unlike the traditional approach of NASA and older aerospace companies that attempt to anticipate all of the engineering problems before a test flight. That leads to more failures, but SpaceX has shown it can be faster and more efficient.But the seventh, eight and ninth test flights were disappointing, because the upper-stage Starship failed at an earlier part of the flight than on the fifth and sixth test flights, which survived re-entry and simulated a landing over the Indian Ocean. On the 10th flight the booster successfully simulated a soft landing over the Gulf of Mexico, and the upper-stage made it all the way to the Indian Ocean. While in space, the upper stage deployed eight dummy prototypes of SpaceX’s next-generation Starlink internet satellites, successfully testing a Pez dispenser-like apparatus to push each one into space.After setbacks during the last three launches of Starship, Elon Musk’s rocket splashed down in the Indian Ocean on Tuesday night.
We’re discussing why the new string of apparent QC failures on Falcon 9. Are you maybe trying to argue it’s statistics or probability instead but missing the wording? Legitimate question 🤷♂️ · To me, and this is coming from a fan of SpaceX and the Starship program since StarHopper ...
We’re discussing why the new string of apparent QC failures on Falcon 9. Are you maybe trying to argue it’s statistics or probability instead but missing the wording? Legitimate question 🤷♂️ · To me, and this is coming from a fan of SpaceX and the Starship program since StarHopper lost its nosecone, anyone with a brain and paying attention currently should be able to see that Elon is kind of unraveling, becoming unhinged, and undoing a fair bit of progress his companies have made.The same runaway capitalistic urge to hoard over $400bn of net worth, to become as grossly and immorally rich as possible, is entirely relevant and core to the reason behind the “recent string of failures and delays at SpaceX” that this post is discussing.Now for my TinFoil Hat moment, so people understand that I'm not 100% serious, I would not be totally shocked if it was discovered that someone was actively sabotaging SpaceX from within. Thanks for listening to TinFoil Hat moment. This does come down to more of a complacency issue, so many launches without issues or failures will tend to result in one showing up.This is, I think, where NASA started to be viewed as sluggish and inept, when in reality they were probably being overly-cautious on all projects, new and old, because of worry about failure. SpaceX are in the stage where they probably need to move into slow-and-deliberate territory for Starship while keeping staff on-task on the Falcon side where they have all the experience.

Despite this being Starship's greatest progress to date, the spacecraft sprang leaks, spun out of control and broke up in orbit.
Ultimately, though, Starship's ninth test flight became its third in a row to end in fiery failure. Space X has a strong record of reliability with its most successful rocket, the Falcon 9. However, three fumbled missions months apart might leave some observers to wonder: is it all going wrong for SpaceX's Starship?Elon Musk's giant rocket, earmarked for use in a 2027 mission to the Moon, has had multiple catastrophic failures in previous launches. ... The Sedgefield-based company will supply satellite technology to Starlink in a £43.7m deal. ... The four-person crew, who launched a day late due to weather, will relieve members of the previous SpaceX mission onboard the station.Hopes were high for a successful SpaceX Starship mission after two explosive failed launches in January and March.Although for Dr McDowell, the "big failure" was that SpaceX could not maintain the Starship's "attitude - it's pointing direction - during the orbital coast".


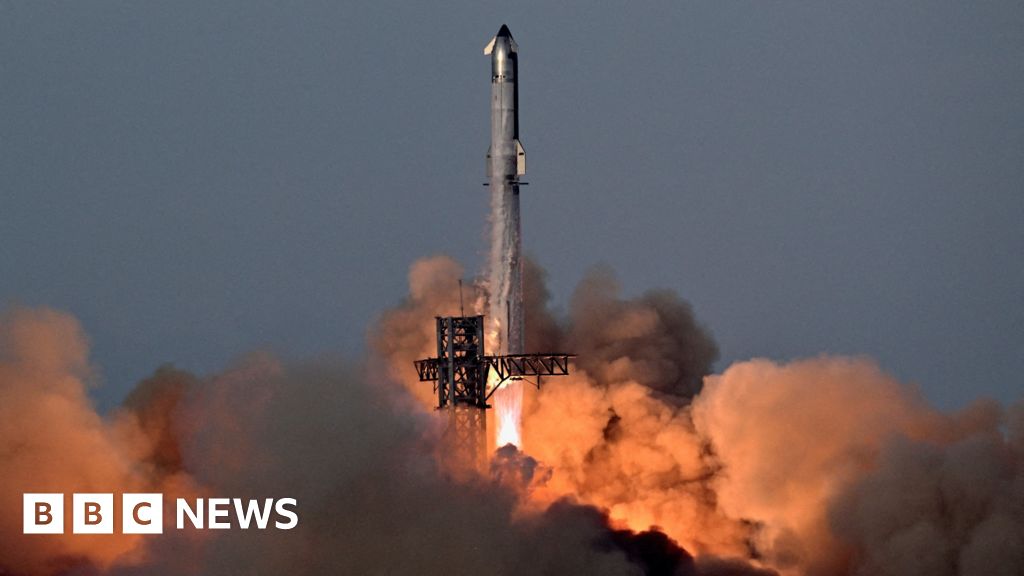
Launches & Spacecraft SpaceX moves giant Super Heavy rocket to pad ahead of Starship Flight 10 launch (photos) ... Starship's Flight 9 failures were traced to booster stress and a pressurization fault.
SpaceX led the probe into the mishap with oversight from the FAA and support from the U.S. Space Force, NASA and the National Transportation and Safety Board. Investigators traced the failures to separate structural issues in each of the vehicle's stages, according to a recent SpaceX statement.In the same update, SpaceX also shared findings about the explosion that occurred on June 18, at one of Starbase's ground test sites. The incident destroyed Ship 36, the upper stage previously tapped for Starship's upcoming launch, as well as the surrounding infrastructure. ... Flight 9 was the third Starship launch of 2025. On all three occasion, the upper stage failed to achieve its main mission goals.Final telemetry was received as the spacecraft was descending over the Indian Ocean, where SpaceX had been hoping the vehicle would make a controlled splashdown. Investigators say the cause of Ship 35's issues could be traced to a failure in a gas diffuser used to pressurize the main fuel tank, which engineers were able to replicate at SpaceX's test site in McGregor, Texas.SpaceX traced the root cause to a composite overwrapped pressure vessel (COPV), used to store nitrogen in Starship's payload bay. The failure was caused by "undetectable or under-screened damage" to the COPV, which compromised the vehicle's structure and caused the propellant leak and subsequent explosion on the stand.
SpaceX designs, manufactures and launches advanced rockets and spacecraft.
SpaceX designs, manufactures and launches advanced rockets and spacecraft. The company was founded in 2002 to revolutionize space technology, with the ultimate goal of enabling people to live on other planets.


SpaceX said, "The vehicle was in the process of loading cryogenic propellant for a six-engine static fire when a sudden energetic event resulted in the complete loss of Starship and damage to the immediate area surrounding the stand." An analysis by the company found that the likely cause was the failure ...
SpaceX said, "The vehicle was in the process of loading cryogenic propellant for a six-engine static fire when a sudden energetic event resulted in the complete loss of Starship and damage to the immediate area surrounding the stand." An analysis by the company found that the likely cause was the failure of a pressurized tank that stores gaseous nitrogen for the ship's environmental control system, which triggered the explosion.That explosion occurred less than a month after test flight nine ended prematurely when the "Starship experienced a rapid unscheduled disassembly" due to mechanical failures early in the flight, according to SpaceX.Test flight eight in March ended after what SpaceX described as a "hardware failure" with one of the upper-stage Raptor engines, leading to fuel igniting where it shouldn't have. The company believes the vehicle then automatically self-destructed.To receive NASA's sign-off, SpaceX will have to show that Starship and its Super Heavy booster "can tolerate failures, provide life-sustaining environments, and offer the crew sufficient control and situational awareness." A spacecraft must be safe enough to meet NASA's goal of keeping the loss of a crew to 1 in 500 during launches and landings.
SpaceX has pulled off a successful test flight of its newest generation rocket Starship, reversing a trend of disappointing failures.
SpaceX's mantra has been to fail fast, learn fast.But after three failures in a row this year, questions were being asked about the future of SpaceX and about whether Mr Musk had been spending too much time on US politics."Great work by the SpaceX team!!", posted SpaceX CEO Elon Musk on X, who is spending billions on developing Starship, which each launch costing an estimated $100m. He will be welcoming the success after three Starship launches ended in spectacular failure this year, and one rocket exploded on its test stand in June.The Starship rocket is critical to the company's hopes of one day carrying people to the Moon and Mars.


NASA changes the rules of the game for commercial space stations · ISS is still leaking air after latest repair efforts fail
SpaceX's Dragon spacecraft has successfully reboosted the International Space Station (ISS), raising the perigee of its orbit by approximately one mile and further eroding the complex's reliance on Russian rocketry.The reboost kit, located in the trunk of the SpaceX CRS-33 Dragon cargo spacecraft, consists of two Draco engines.The system is isolated from the rest of the spacecraft, and the demonstration was intended to show how the vehicle can maintain the ISS's altitude.The Northrop Grumman Cygnus cargo spacecraft can also perform limited reboosts, and SpaceX demonstrated in 2024 that the Dragon itself is capable of using its engines to nudge the ISS.

SpaceX determined that "the vehicle was in the process of loading cryogenic propellant for a six-engine static fire when a sudden energetic event resulted in the complete loss of Starship and damage to the immediate area surrounding the stand." An analysis by the company found that the likely cause was the failure ...
SpaceX determined that "the vehicle was in the process of loading cryogenic propellant for a six-engine static fire when a sudden energetic event resulted in the complete loss of Starship and damage to the immediate area surrounding the stand." An analysis by the company found that the likely cause was the failure of a pressurized tank that stores gaseous nitrogen for the ship's environmental control system, which triggered the explosion.That explosion occurred less than a month after test flight nine ended prematurely when the "Starship experienced a rapid unscheduled disassembly" due to several mechanical failures minutes into the flight, according to SpaceX.Test flight eight in March ended after what SpaceX described as a "hardware failure" with one of the upper-stage Raptor engines, leading to fuel igniting where it shouldn't have. The company believes the vehicle then automatically self-destructed.That pace is central to SpaceX's iterative engineering process, which de Weck describes as "rapid prototyping or agile engineering." "We'll find problems, we'll test it rapidly, and we'll fix it as we go. And we gradually approach a perfect product. That does not work as well for safety-critical systems and where the cost of failure is high," de Weck said.
Spectators watch SpaceX's Starship SN8 prototype launch from South Padre Island, Texas on December 9, 2020. (Image credit: Forest Katsch via Wikimedia Commons) This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to Space.com's Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights. This was the ninth test flight for the rocket, and the third catastrophic failure ...
Spectators watch SpaceX's Starship SN8 prototype launch from South Padre Island, Texas on December 9, 2020. (Image credit: Forest Katsch via Wikimedia Commons) This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to Space.com's Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights. This was the ninth test flight for the rocket, and the third catastrophic failure in a row, just this year.Is this what we should expect from the very ship some are counting on to take humans further than we’ve ever been in the solar system? Or does this failure point to deeper concerns within the broader program? ... SpaceX reached space with Starship Flight 9 launch, then lost control of its giant spaceship (video)On this particular test flight, as Starship positioned itself for atmospheric reentry, one of its 13 engines failed to ignite. Shortly after, a booster appeared to explode, leading to a complete loss of control. The rocket ultimately broke apart over the Indian Ocean, which tonnes of debris will now call home. The headquarters for the private space company SpaceX's factories are based in Hawthorne, California.For example, a failed test flight in 2023 left the town of Port Isabel, Texas, which is located beside the launch site, shaking and covered in a thick cloud of dirt. Debris from the exploded rocket smashed cars. Residents told the New York Times they were terrified. They also had to clean up the mess from the flight. Then, in September 2024, SpaceX was fined by the US Environmental Protection Agency and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality for 14 separate incidents since 2022 where the launch facilities discharged polluted water into Texas waterways.








